Get our FREE GUIDE to nonprofit financial reports, featuring illustrations, annotations, and insights to help you better understand your organization’s finances. In fact, the IRS doesn’t issue requirements for nonprofits to be audited, but other federal and state agencies do in some circumstances. For example, if your nonprofit is based in California and you have a gross income of $2 million or more, you will be required to get annual audits. The federal government is not the only one that requires regular audits by nonprofits. One-third of all states in the US need nonprofits to perform regular audits if they solicit state residents. This type of audit generally addresses issues with your tax return, discrepancies between your organization’s and freelancers’ or employee returns, or if a division of the IRS issues an IRS-wide examination.
Testing Compliance with Policies
A nonprofit’s compliance with tax laws and reporting requirements is central to maintaining tax-exempt status and avoiding penalties. Absent the curiosity of the IRS, nonprofit leaders may seek audited financial records for other reasons. A nonprofit audit might result from a judicial directive or another agency request, e.g., an agency granting federal funding. Just like you’d visit a doctor to ensure everything’s running smoothly with your body, an audit ensures that your nonprofit’s financial health is in tip-top shape. It’s a comprehensive examination of your financial statements and processes by an independent auditor to verify that everything is accurate and complies with the law. Major donors, government agencies, and corporate partners frequently require audited financials to approve grants or renew an organization’s funding.
- In these cases, the Board should determine which type and frequency of audits to conduct based on the organization’s circumstances.
- Audited financial statements are crucial for ensuring financial transparency and accountability.
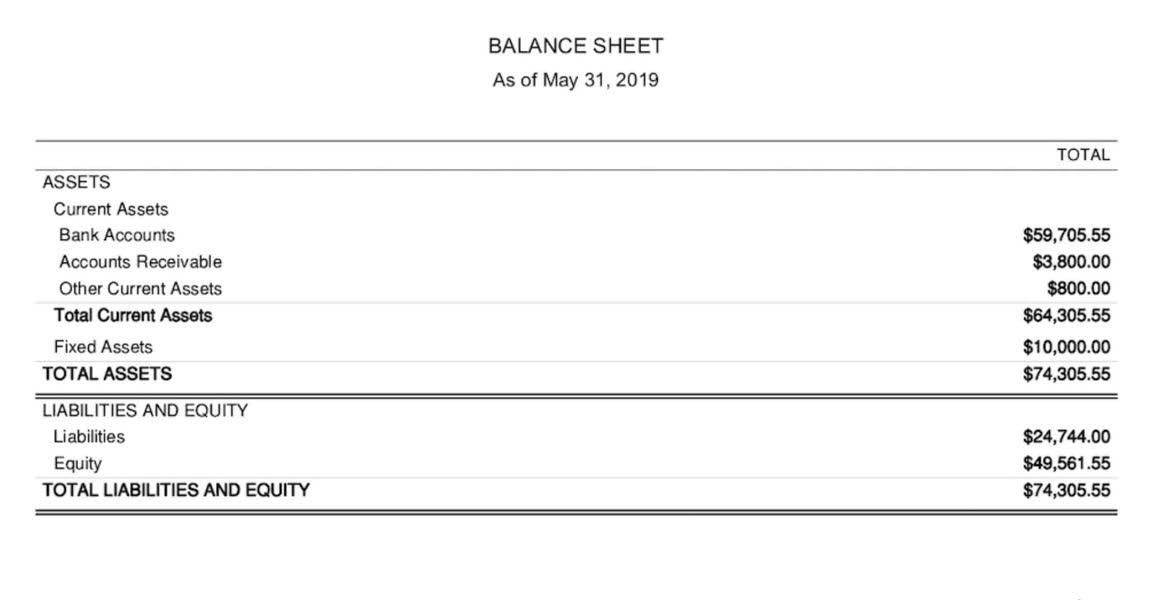
- With FastFund Accounting, you can generate all the required financial statements.
- This article aims to demystify these requirements, providing a clear roadmap to navigate the complexities and ensure your nonprofit remains compliant.
- As per IRS, nonprofits with gross receipts less than $200,000 and total assets less than $500,000 can choose to file Form 990-EZ instead of Form 990.
- Nonprofits often establish their audit requirements within their bylaws to maintain good governance practices.
- VComply is the first unified Governance, Risk, Compliance (GRC)and Compliance & Risk Operating System (CROS) platform foroperational execution and trust.
Nonprofit Audit Guide: Ensure Financial Transparency Today
If your nonprofit does not meet any of the criteria above, an audit is likely not required unless your state has different criteria. We’ll answer the question of whether audits are required or optional and then understand how much audits cost, how long they take, and why you might want to pay for an audit even if it is not required. Learn about Yellow Book Audits, when they’re required, and who needs them. There are individual The Key Benefits of Accounting Services for Nonprofit Organizations auditors or entire audit firms that specialize in the nonprofit sector. It looks at your control procedures, risk management, and adherence to policies.
Trust Your Nonprofit Audit to Lewis.cpa
Audited financial statements are crucial for ensuring financial transparency and accountability. They build trust with donors, grantmakers, and stakeholders by providing assurance that the nonprofit’s financial practices are sound and funds are used appropriately. An independent audit reviews financial statements, including your nonprofit’s statement of financial position, related statement of activities, cash flows and notes to the financial statements. With FastFund Accounting, you can generate all the required financial statements.
See Financial Statements Through Your Accountant’s Eyes!
As mentioned before, an IRS audit of a nonprofit organization is fairly rare. However, they do still happen, so it is good to be aware of the possibility and everything the process entails. Knowing the reasons that organizations do end up getting audited by the IRS is important and can help instruct your organization on ways to operate properly in order to avoid ever being in that situation. It’s crucial to understand what constitutes “contributions” under Illinois law. The term includes “the promise or grant of any money or property of any kind, including the promise to pay (i.e., pledges)”. However, it excludes the sale of tickets by music and dramatic arts organizations for live public performances, union dues, and donated services.
- However, even if your nonprofit isn’t required to undergo an audit, it can still be worthwhile to conduct one to get a better understanding of your organization’s financial situation.
- Depending on the type of audit you need, you might be required to submit other documents.
- Minnesota courts have long held that the law imposes the highest standard of integrity on the bearers of these duties.
- You want some details about their offerings and the manner in which they submit audited financial statements.
- An auditing committee is optional if you have a finance committee, but it may help your organization keep up to date with internal and external audit requirements.
- They not only ensure financial accuracy and compliance but also build stakeholder confidence and enhance overall accountability.
- It shows whether or not your accounting records are accurate per generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP), in the auditor’s professional judgment.
Figuring out if your organization is mandated to obtain an annual audit is an important step in your overall compliance with the guidelines and regulations for nonprofits. If your nonprofit is not required to obtain an audit, you may still consider doing so because of the benefits. Implementing and making changes to your processes and internal controls after an audit can help make future audits even more successful and ease the stresses that these can cause. Whether you’re gearing up for your first audit or looking to streamline a process that’s been inefficient in the past, our professionals can help lay the foundation for a smooth, efficient audit experience. The auditor tests the nonprofit’s adherence to its policies and procedures. This includes reviewing documentation to ensure that all transactions are properly authorized and recorded according to the organization’s policies.
Actively participating in these networks can help nonprofits remain compliant and access a community of shared knowledge. Navigating nonprofit audit requirements can be overwhelming, but professional accounting services make the process easier by ensuring compliance at every step. The time required to complete an audit also depends on the availability of key personnel, the quality of the organization’s accounting records, and the extent to which the organization’s internal controls are effective.